A loose tooth can be an alarming experience — whether it’s due to an injury, gum disease, or biting something too hard. It often starts with a strange sensation when you eat or brush — your tooth moves slightly or feels different from the rest. Ignoring it can lead to further complications, from tooth loss to infection.
If you’re wondering what should be done with a loose tooth, this guide explains every detail — the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and how to prevent it from happening again. Understanding the right steps to take can save your tooth and restore your dental health.
Table of Contents
Understanding What Causes a Loose Tooth
A tooth doesn’t loosen without reason. It’s usually a sign that something deeper is affecting your gums, bone, or bite. Identifying the cause early is the key to saving it.
Gum Disease (Periodontal Disease)
The most common cause of a loose tooth in adults is periodontal disease. This infection damages the gums and bone that hold teeth in place. When bacteria build up along the gum line, they cause inflammation, leading to bone loss and reduced support for your teeth.
You may notice symptoms like bleeding gums, bad breath, gum recession, or shifting teeth. If left untreated, gum disease can result in tooth loss.
Trauma or Injury
An accidental fall, sports injury, or even biting into something hard can loosen a tooth. The ligaments around the tooth can stretch or tear, weakening its stability. Immediate dental attention is necessary to prevent permanent damage.
Bruxism (Teeth Grinding)
Grinding or clenching your teeth, often while sleeping, puts excessive pressure on your teeth and gums. Over time, this pressure wears down the bone structure, making teeth loose or wobbly.
Poor Oral Hygiene and Plaque Buildup
Neglecting brushing and flossing allows plaque to harden into tartar, which irritates the gums and causes inflammation. This leads to gum detachment and weakened support structures.
Hormonal or Health Changes
Pregnancy, menopause, or certain medications can affect your gums and bone density, occasionally causing temporary tooth mobility.
Signs and Symptoms of a Loose Tooth
Recognizing the early warning signs of a loose tooth helps you take action before it worsens.
- Tooth movement when touched or chewing
- Gum swelling or bleeding
- Pain or sensitivity when biting
- Gum recession exposing the tooth root
- A feeling that your bite has shifted
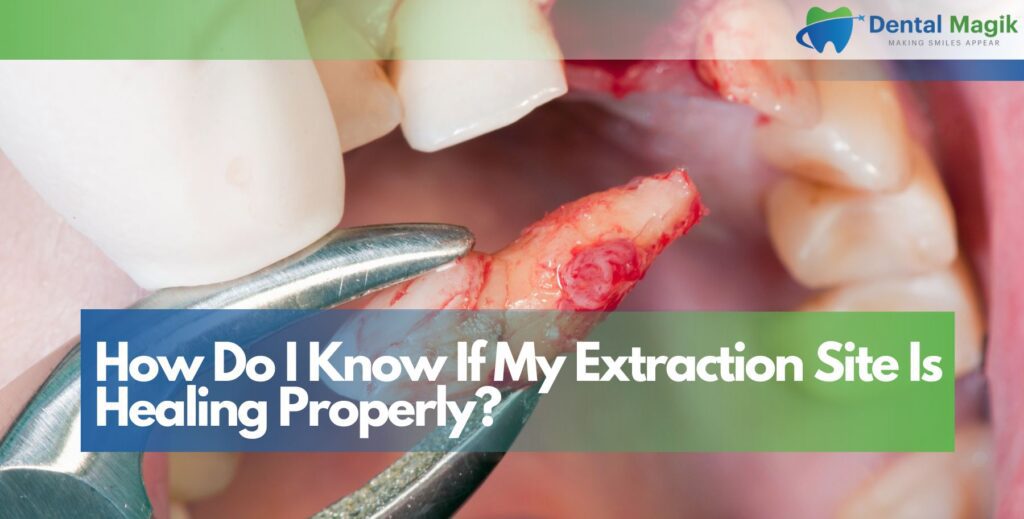
If any of these symptoms appear, contact your dentist immediately. Early treatment can often save the tooth without extraction.
Immediate Steps to Take if You Have a Loose Tooth
If your tooth feels loose, it’s crucial not to panic — but also not to ignore it. The right steps can make a big difference in whether the tooth can be saved.
Avoid Wiggling the Tooth
Do not touch, move, or play with the tooth using your fingers or tongue. This movement can damage surrounding tissues or break the blood vessels needed for healing.
Stick to Soft Foods
Avoid hard, sticky, or crunchy foods that can worsen mobility. Eat soft foods like soup, yogurt, or mashed vegetables until you see your dentist.
Keep the Area Clean
Gently brush and floss around the loose tooth, but be careful not to apply direct pressure. Rinse with warm salt water to reduce inflammation and bacterial buildup.
Avoid Using That Side for Chewing
Chewing on the affected side can increase pressure on the loose tooth, worsening its condition.
See Your Dentist Immediately
A dentist will assess whether the tooth can be stabilized or needs further treatment like splinting, scaling, or bone grafting.
Professional Treatments for a Loose Tooth
Once you visit your dentist, they’ll evaluate the cause and recommend the best solution based on your oral condition.
Scaling and Root Planing
If gum disease is the culprit, your dentist will perform deep cleaning — scaling and root planing. This removes plaque and bacteria from below the gum line, helping gums reattach and stabilize the tooth.
Tooth Splinting
In mild to moderate cases, your dentist may use a splint — a small wire or composite material — to bond the loose tooth to adjacent stable teeth. This allows the tooth to heal and regain its support.
Bone Grafting or Gum Surgery
If bone loss has occurred, a bone graft may be performed to rebuild the jaw structure. In cases of severe gum recession, gum grafting helps restore tissue support.
Bite Adjustment
If grinding or uneven bite pressure is causing the problem, your dentist may reshape parts of the tooth or fit you with a night guard to prevent damage during sleep.
Tooth Extraction (Last Resort)
If the tooth cannot be saved due to extreme infection or bone loss, extraction may be necessary. The dentist will then recommend replacement options like dental implants, bridges, or partial dentures to restore alignment.
How Dentists Diagnose a Loose Tooth
Your dentist will perform several diagnostic steps:
- Visual and physical examination to check gum health and tooth stability
- X-rays to evaluate bone loss and surrounding structures
- Periodontal probing to measure pocket depth around the gums
- Mobility grading, which classifies how loose the tooth is (Grade 1–3)
Based on these results, a personalized treatment plan is designed to stop the progression and restore strength.
Home Remedies and What to Avoid
While home care can support healing, it cannot replace professional treatment. However, following these steps can prevent worsening.
Salt Water Rinse
Rinsing with warm salt water helps reduce bacteria and soothe inflamed gums. Do this twice daily.
Hydrogen Peroxide Mouthwash
A diluted hydrogen peroxide rinse (only under dentist’s recommendation) can kill harmful bacteria and support gum healing.
Turmeric or Aloe Vera Gel
Both have anti-inflammatory properties that can help soothe gums temporarily.
Avoid Misleading Home Hacks
Do not try to pull, push, or “tighten” the tooth yourself. Avoid using over-the-counter glue or adhesives. These can lead to infection or irreversible damage.
How Gum Disease Leads to Tooth Loosening
Gum disease weakens the tissues and bone that support your teeth. As bacteria accumulate beneath the gum line, inflammation damages the ligaments holding the tooth in place. Over time, this leads to bone loss and gum recession, making teeth loose, sensitive, and at risk of falling out without timely treatment.
Early Stage – Gingivitis
Plaque buildup irritates gums, causing redness and bleeding. At this stage, the damage is reversible with proper cleaning.
Moderate Stage – Periodontitis
Infection spreads below the gum line, destroying bone and ligament support. Teeth start feeling loose and shift slightly.
Advanced Stage – Severe Periodontitis
Severe bone loss leads to tooth movement, gum recession, and even tooth loss. At this stage, intervention such as grafting or surgery is essential.
Maintaining good oral hygiene and regular dental visits can stop gum disease before it reaches these stages.
Loose Tooth from Injury or Accident
If your loose tooth results from a blow, fall, or trauma, time is critical.
What to Do Immediately
- Avoid touching or moving the tooth
- Rinse your mouth with warm water
- Apply a cold compress on the face to reduce swelling
- Visit your dentist or an emergency dental clinic within 30 minutes
Treatment Options After Injury
- Stabilization splinting for 2–4 weeks
- Root canal therapy if the nerve is damaged
- Soft diet and anti-inflammatory medication during healing
Quick action greatly improves the chances of saving the tooth.
Bruxism and Its Connection to Loose Teeth
Chronic teeth grinding or clenching, known as bruxism, can gradually loosen teeth by applying constant stress on the supporting bone and gums.
Signs You Might Have Bruxism
- Jaw pain or headaches upon waking
- Worn-down tooth enamel
- Clicking or tight jaw muscles
Treatment Options
- Custom-made night guards to prevent grinding
- Stress management techniques to reduce clenching
- Orthodontic adjustments if the bite is uneven
By managing bruxism, you protect both the alignment and longevity of your teeth.
Preventing a Loose Tooth in the Future
Preventive care is always better than treatment. Keeping your gums and bone strong ensures teeth remain stable for life.
Maintain Excellent Oral Hygiene
Brush twice daily, floss, and use antibacterial mouthwash to prevent gum infection.
Regular Dental Visits
Routine cleanings and checkups allow your dentist to catch gum issues or bone loss early.
Balanced Diet
Calcium, vitamin D, and phosphorus strengthen teeth and bones. Avoid excessive sugar and acidic foods.
Protective Mouthguards
If you play sports or grind your teeth, wearing a mouthguard can prevent trauma or stress on teeth.
Quit Smoking
Smoking restricts blood flow to the gums, delaying healing and worsening gum disease.
Long-Term Treatments After Tooth Stabilization
Once your loose tooth is treated and stable, your dentist may recommend long-term care to strengthen your oral foundation.
Orthodontic Evaluation
Misaligned teeth or an improper bite can cause uneven stress, leading to future loosening. Orthodontic correction can prevent recurrence.
Bone Regeneration Procedures
Modern bone grafting techniques help restore lost bone mass, creating stronger support for your teeth.
Regular Periodontal Maintenance
Patients who’ve had gum disease require professional cleanings every 3–4 months to maintain stability.
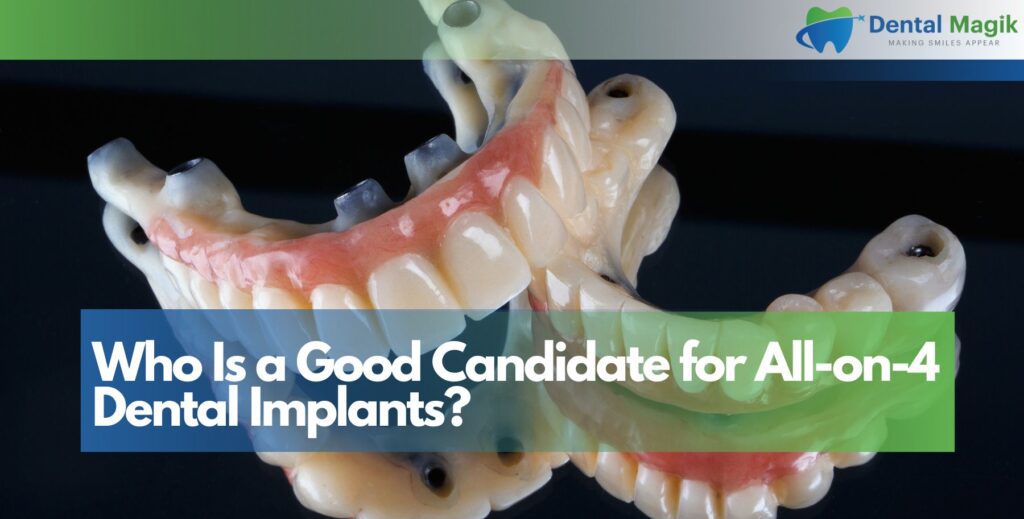
When a Loose Tooth Cannot Be Saved
Despite the best efforts, some teeth cannot be salvaged due to severe bone loss, infection, or trauma. In such cases, replacing the tooth becomes necessary.
Dental Implant
A dental implant replaces the tooth root and integrates with your jawbone, offering a permanent solution that maintains alignment and prevents bone loss.
Dental Bridge
A bridge uses neighboring teeth as anchors to replace the missing tooth, restoring both function and aesthetics.
Partial Denture
For multiple missing teeth, a removable partial denture can restore your smile temporarily or permanently.
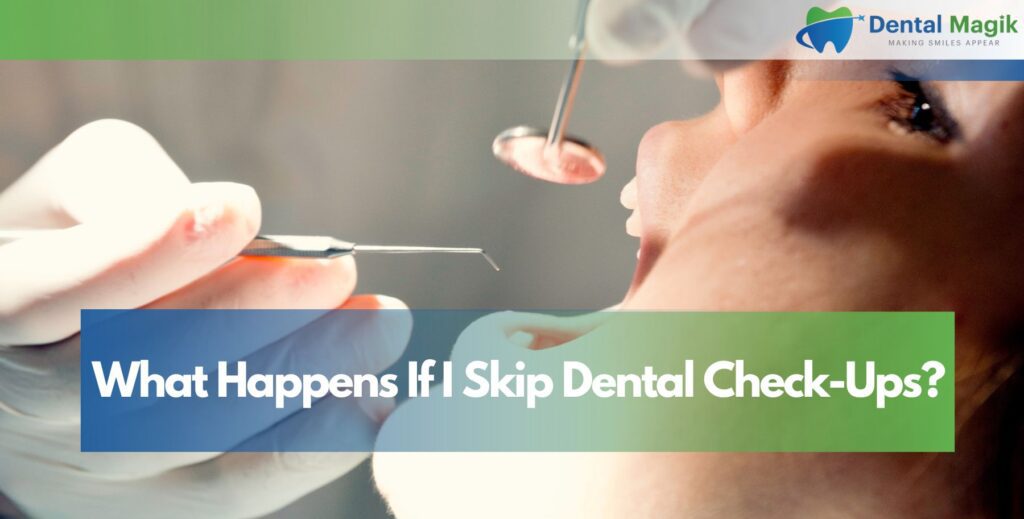
What Happens If a Loose Tooth Is Ignored?
Neglecting a loose tooth can have serious consequences. Over time, bacteria invade the loosened area, causing infection, bone damage, and eventual tooth loss.
Ignoring treatment may also affect nearby teeth, leading to misalignment or bite changes. Early dental intervention is always the best way to avoid complex, costly procedures later.
How Dentists Save a Loose Tooth
A dentist uses various modern treatments depending on your diagnosis:
- Stabilization splinting to support the tooth
- Antibiotics or deep cleaning to treat infection
- Bone or gum grafts to rebuild lost structure
- Night guards to control grinding stress
With timely care, most loose teeth can be restored to full stability.
Healing and Recovery After Treatment
The recovery process depends on the treatment performed. Most patients experience minor soreness for a few days.
To speed up healing:
- Follow your dentist’s care instructions
- Avoid chewing hard foods
- Maintain oral hygiene
- Attend all follow-up appointments
Healing gums and bone tissues usually take several weeks, but full stabilization can last a few months.
Conclusion
A loose tooth should never be ignored. Whether it’s caused by gum disease, trauma, or teeth grinding, timely action can prevent tooth loss and restore your oral health. Maintaining strong gums and bones through good hygiene and regular checkups is the best defense against loose teeth.
If you notice mobility in any of your teeth, visit an experienced Dentist in East Brunswick, NJ for a thorough evaluation and treatment plan. Early intervention ensures you keep your natural teeth healthy and stable for years to come.
FAQs
Can a loose tooth tighten back up on its own?
A mildly loose tooth can sometimes reattach naturally if the cause is minor trauma. However, most cases need professional treatment to ensure proper healing.
Should I pull out a loose adult tooth?
No. Never pull an adult tooth on your own. Doing so may cause infection or permanent bone damage. Always consult your dentist.
Can gum disease cause permanent tooth loss?
Yes. Untreated gum disease destroys the bone supporting your teeth, eventually leading to tooth loss.
How long does it take to stabilize a loose tooth?
It depends on the severity. With splinting and treatment, it may take a few weeks to a few months for full stability.
What foods should I avoid with a loose tooth?
Avoid crunchy, sticky, or hard foods such as nuts, candy, and ice until your dentist confirms recovery.
Is a loose tooth always painful?
Not necessarily. Some loose teeth don’t cause pain initially but can become sensitive or sore as the condition worsens.
Can stress cause loose teeth?
Indirectly, yes. Stress-related grinding (bruxism) can weaken tooth support and cause mobility over time.
Can a dental implant replace a lost tooth permanently?
Yes. Dental implants offer a permanent, natural-looking replacement that prevents bone loss and keeps your smile aligned.