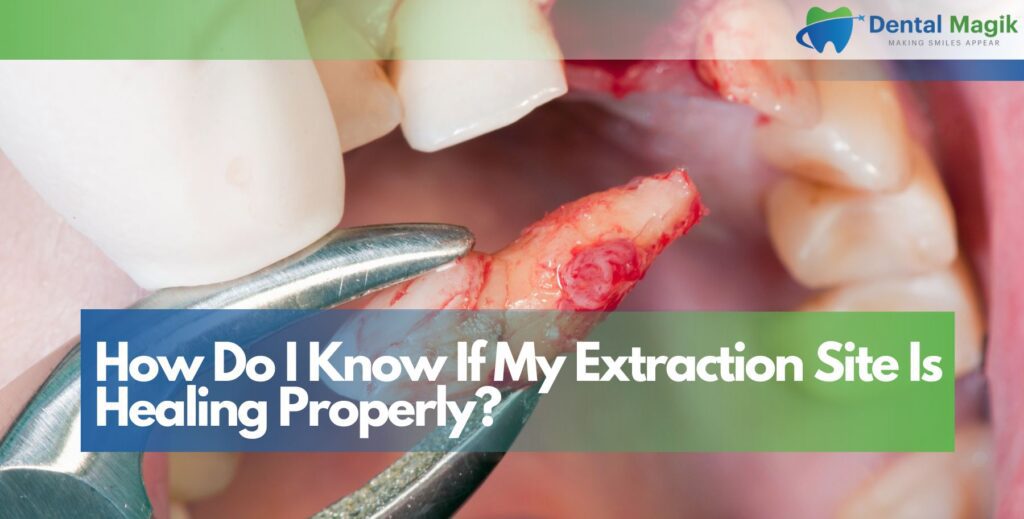
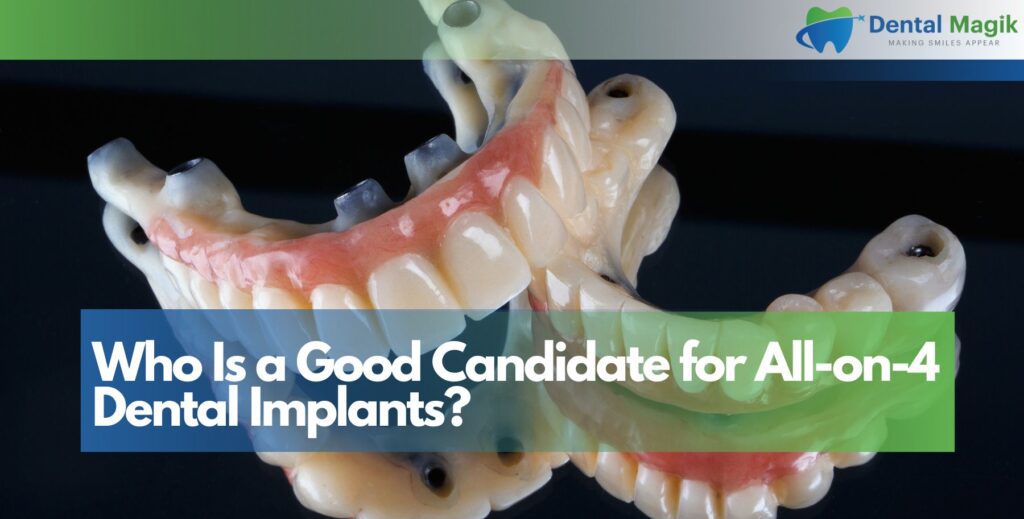
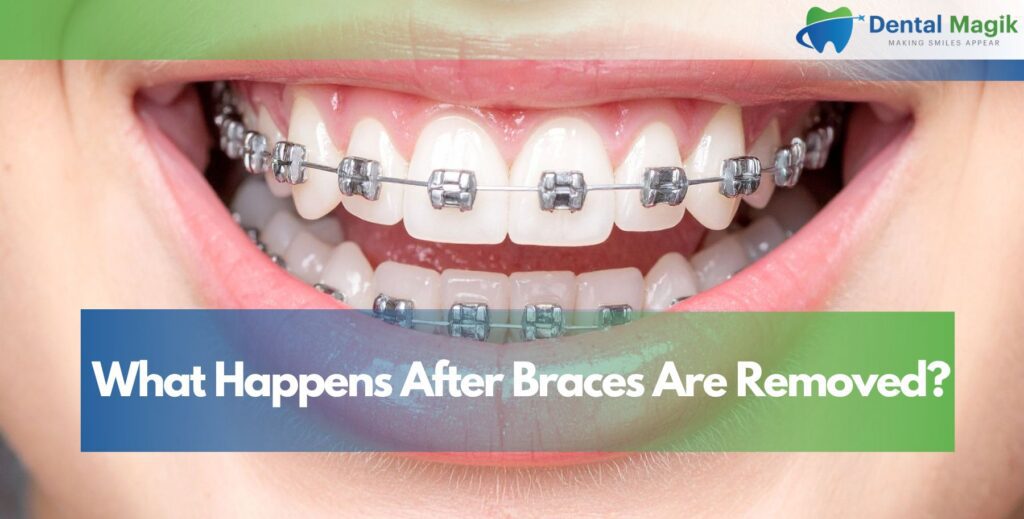
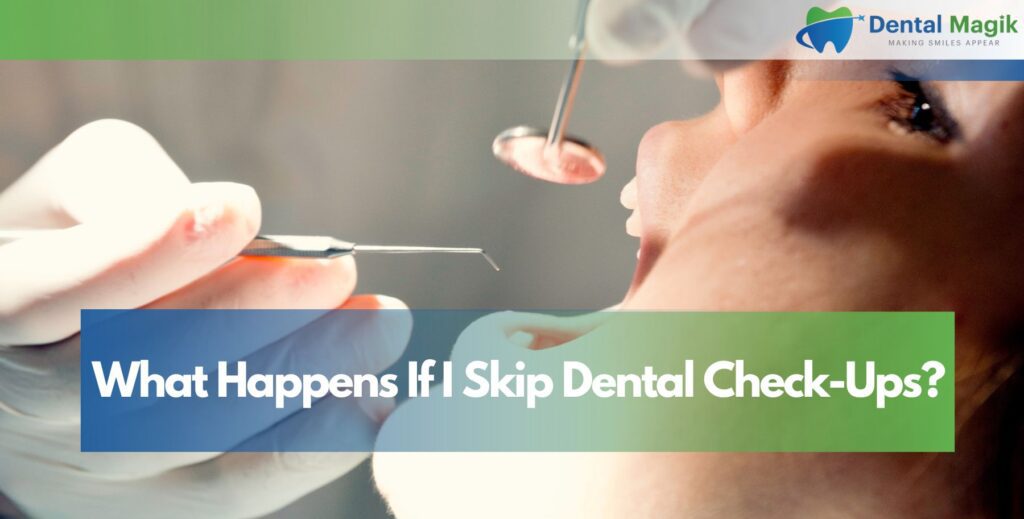
Losing a tooth can affect your smile, speech, and confidence. One of the most common and reliable solutions is a dental bridge. It restores missing teeth by “bridging” the gap using crowns and supporting teeth on either side.
Before you decide to get a bridge, it’s important to understand what it involves, how it works, and what to expect during and after treatment. This guide walks you through everything you need to know before getting a dental bridge — from benefits and types to costs, care, and long-term maintenance.
Table of Contents
What Is a Dental Bridge and How Does It Work?
A dental bridge is a fixed dental restoration used to replace one or more missing teeth. It consists of artificial teeth, called pontics, held in place by crowns placed on the surrounding natural teeth or implants.
The bridge restores your ability to chew and speak properly while maintaining the natural shape of your face. It prevents nearby teeth from drifting into empty spaces, which helps keep your bite aligned. A bridge also improves aesthetics, giving you a natural-looking, confident smile.
Types of Dental Bridges You Can Choose From
There are several types of dental bridges, and the right choice depends on your oral condition, number of missing teeth, and budget.
Traditional Dental Bridge
The most common type involves placing crowns on both sides of the missing tooth and attaching a false tooth in between. It’s durable and ideal for patients with strong adjacent teeth.
Cantilever Bridge
A cantilever bridge uses only one supporting tooth next to the missing tooth. It’s less common today because it puts extra pressure on a single supporting tooth, making it suitable only for specific cases.
Maryland (Resin-Bonded) Bridge
This bridge is attached using a metal or porcelain framework bonded to the back of the adjacent teeth. It’s less invasive and doesn’t require full crowns, making it a conservative option for front teeth.
Implant-Supported Bridge
Instead of using natural teeth for support, this type is anchored to dental implants. It’s one of the strongest and longest-lasting solutions but also the most expensive and time-intensive to place.
Who Is a Good Candidate for a Dental Bridge?
A dental bridge isn’t suitable for everyone. Your dentist will assess your overall oral health, gum condition, and bone strength before recommending treatment.
Healthy Adjacent Teeth
Bridges rely on nearby teeth for support. These teeth must be healthy, free of decay, and strong enough to hold the crowns.
Good Oral Hygiene
Candidates must be committed to regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups. Poor oral hygiene can lead to gum disease, which weakens the bridge over time.
Stable Bite Alignment
If your bite is misaligned, your dentist may need to correct it first to ensure the bridge fits comfortably and functions properly.
No Untreated Gum Disease
Healthy gums are essential for bridge stability. If you have periodontal issues, your dentist will treat them before the procedure.
Steps Involved in Getting a Dental Bridge
The process of getting a dental bridge usually takes two or more visits to your dentist. Each step plays a vital role in achieving a comfortable and natural result.
Initial Consultation and Examination
Your dentist will evaluate your mouth, take X-rays, and discuss different bridge options. They’ll assess your supporting teeth and gums to ensure they can handle the bridge.
Tooth Preparation
The adjacent teeth are reshaped slightly to accommodate the crowns. Local anesthesia is used for comfort during this process.
Impressions and Temporary Bridge
An impression of your teeth is taken to create a custom-fit bridge. Meanwhile, a temporary bridge is placed to protect your exposed teeth and gums.
Placement of the Permanent Bridge
Once your permanent bridge is ready, your dentist removes the temporary one, checks the fit, and permanently cements the bridge in place.
Follow-Up and Adjustments
Your dentist may schedule a follow-up visit to ensure the bridge fits perfectly and feels natural when chewing or speaking.
Benefits of Getting a Dental Bridge
Choosing a dental bridge comes with multiple benefits that go beyond filling a gap in your smile.
Restores Chewing and Speaking Ability
Missing teeth can make chewing difficult and affect pronunciation. A bridge restores normal function and makes eating and speaking easier.
Improves Appearance and Confidence
A well-crafted bridge looks natural and matches your existing teeth. It enhances your smile and boosts confidence.
Prevents Teeth Shifting
Bridges maintain alignment by preventing surrounding teeth from moving into the empty space, reducing the risk of bite problems and jaw discomfort.
Provides Long-Term Stability
When properly maintained, a dental bridge can last 10 to 15 years or longer, offering a strong, reliable replacement for missing teeth.
Potential Drawbacks to Consider
While bridges offer many benefits, understanding their limitations helps you make an informed decision.
Requires Alteration of Healthy Teeth
To support the bridge, your dentist must file down adjacent teeth to fit crowns. This is a permanent alteration.
Risk of Decay or Gum Disease
Improper cleaning around the bridge can lead to decay on supporting teeth or gum infection.
Limited Lifespan Compared to Implants
Although durable, bridges don’t last as long as implants. Over time, they may need replacement due to wear or gum recession.
How Long Do Dental Bridges Last?
The longevity of a dental bridge depends on oral hygiene, material quality, and regular dental check-ups.
Average Lifespan
A well-maintained bridge typically lasts between 10 and 15 years, though some last over 20 years.
Factors That Affect Durability
- Oral hygiene habits
- Quality of the dental material used
- Bite pressure and chewing habits
- Frequency of professional cleanings
How to Extend the Life of Your Bridge
Brush twice daily, floss under the bridge using a threader, and visit your dentist every six months for cleanings and inspections.
Dental Bridge vs. Dental Implant: Which Is Better?
Both options restore missing teeth but differ in procedure, cost, and longevity.
Procedure Differences
A bridge relies on adjacent teeth for support, while an implant is surgically inserted into the jawbone.
Cost Comparison
Bridges are generally less expensive upfront, but implants offer better long-term value because they can last a lifetime with proper care.
Bone Preservation
Implants prevent bone loss, while bridges do not. If bone health is a priority, implants might be the better choice.
Aesthetic Appeal
Both provide natural-looking results, but implants more closely mimic natural tooth structure.
Maintenance Tips for Dental Bridges
Keeping your dental bridge clean and strong is essential for long-term success.
Brush and Floss Regularly
Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and non-abrasive toothpaste. Floss daily with a floss threader to clean underneath the bridge.
Avoid Sticky and Hard Foods
Chewing sticky candy or hard nuts can damage your bridge or loosen the crowns.
Regular Dental Check-Ups
Your dentist will inspect your bridge, clean hard-to-reach areas, and ensure your gums remain healthy.
Use Antibacterial Mouthwash
Rinsing helps reduce bacteria buildup and maintain gum health.
Cost of Getting a Dental Bridge
The cost of a dental bridge in the U.S. typically ranges between $1,500 and $5,000 per bridge, depending on type, material, and location.
Factors Affecting Cost
- Type of bridge (traditional, cantilever, or implant-supported)
- Material used (porcelain, metal, or zirconia)
- Number of missing teeth
- Complexity of the procedure
Does Insurance Cover Dental Bridges?
Many dental insurance plans cover a portion of the bridge cost, especially if it’s medically necessary. Confirm coverage with your provider before treatment.
What to Expect After Getting a Dental Bridge
After getting a dental bridge, you may experience mild soreness or sensitivity as your mouth adjusts. Speaking and chewing might feel different for a few days, but this improves quickly. Following good oral hygiene and attending follow-up appointments ensures your bridge settles comfortably and lasts for many years.
Mild Sensitivity
It’s normal to feel slight sensitivity for a few days as your mouth adjusts.
Adaptation Period
Your bite and speech may feel different at first, but you’ll quickly adapt within a week or two.
Follow-Up Care
Regular check-ups help your dentist ensure your bridge remains stable and functional.
Conclusion
Getting a dental bridge is a reliable and effective way to restore missing teeth and improve your smile. Understanding the procedure, maintenance, and long-term expectations helps you make an informed choice that fits your lifestyle and oral health needs.
If you’re ready to explore your options, schedule a consultation with a trusted Dentist in East Brunswick, NJ to receive personalized advice and expert care tailored to your smile.
FAQs
How long does it take to get a dental bridge?
It usually takes two to three appointments over two weeks to complete the procedure, depending on your dentist and the type of bridge.
Is getting a dental bridge painful?
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia, so you’ll feel minimal discomfort. Some mild soreness may occur after the treatment.
Can I eat normally after getting a dental bridge?
Yes. After a few days of adjustment, you can eat most foods. However, it’s best to avoid sticky or hard foods that might damage the bridge.
How do I clean under my dental bridge?
Use a floss threader or special interdental brushes to clean beneath the pontic and around the crowns daily.
Are dental bridges permanent?
Yes, bridges are fixed restorations and can only be removed by a dentist. They can last 10–15 years or more with proper care.
Do dental bridges look natural?
Absolutely. Modern bridges are designed to match your tooth color, shape, and size, providing a seamless look.
What happens if I don’t replace a missing tooth?
Missing teeth can lead to shifting, bite issues, jawbone loss, and changes in facial structure over time.
Can I switch from a bridge to an implant later?
Yes, if your bone structure is healthy enough, you can replace your bridge with implants in the future.